How do dentists treat gum disease?
Treatment of periodontal disease begins with the removal of plaque and tartar. A common first step is scaling and root planning which seeks to remove tartar by scraping it from the surface of each tooth. The problem with tartar or dental calculus as it’s more formally known, is that it contains harmful bacteria. The recommended method of removing tartar is a dentist administered teeth cleaning, or what Deep Dental calls hygiene therapy.
The photos at the side of the page expand when clicked and show the many signs and symptoms of gum disease. This page covers the following topics of interest related to the treatment of periodontal disease:
Gingivitis is the most common form of periodontal disease (non-destructive). It is when there’s an inflammation of the gum tissue. When plaque builds up on the surface, it’s called plaque-induced gingivitis. If left untreated, it can escalate to the destructive form, Periodontitis, which affects the tissues that support and surround the teeth. With poor oral care, bacteria can infiltrate the gum line and affect the underlying bone. If left untouched, it can lead to damage of the teeth’s supporting tissues, loosened teeth, and eventually lost teeth.
What is periodontal disease?
Periodontitis is also called gum disease and is a result of serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue of the mouth. Without proper treatment in the early stages of the disease, periodontal disease can destroy the bone that supports your teeth. Periodontitis can cause teeth to loosen and lead to tooth loss. Periodontitis accounts for more tooth loss among adult Canadians than cavities or accidents.
Periodontitis is very common, especially with seniors, but it is largely preventable.
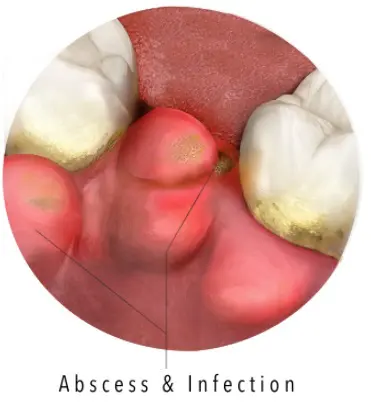
What are signs of gum disease?
1. Swollen or puffy gums, painful chewing
2. Bright red, dusky red or purplish gums
3. Gums that feel tender when touched
4. Gums that bleed easily
5. Pink-tinged toothbrush after brushing
6. Spitting out blood when brushing or flossing your teeth
7. Bad breath
8. Pus between your teeth and gums
9. Loose teeth or loss of teeth
10. New spaces developing between your teeth
11. Gums that pull away from your teeth (recede), making your teeth look longer than normal
12. A change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
People who experience any of these symptoms should contact Deep Dental as soon as possible.
What are the signs of Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is a common and mild form of gum disease, or periodontal disease that causes irritation, redness and swelling of patients’ gingiva, the part of the gum around the base of the teeth.
Some signs a dental patient suffers from gingivitis include,
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Occasional bleeding and comfort while brushing or flossing
- Bad breath
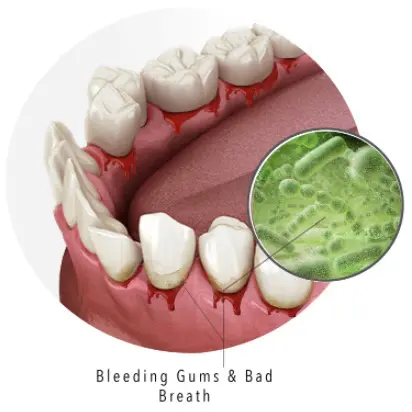
What are the signs of Periodontitis?
Signs a dental patient suffers from periodontitis, or gum disease, include,
- Painfully red and swollen gums
- Frequent bleeding while brushing or flossing
- Gums that pull away from the teeth
- Persistent bad breath or a constant metallic taste in patient’s mouth
- Loose or separating teeth
- An alteration in the way the patient’s teeth fit together
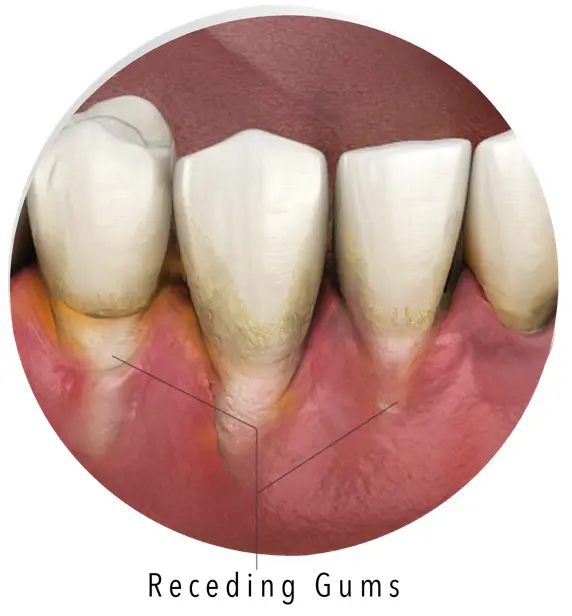
How long does it take for gum disease to develop?
1. First Signs of Gingivitis
2. Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the name applied to early-stage gum disease, and stage two is where it’s usually first noticed and labelled as a condition by dentists. The plaque on the patient’s teeth has begun to accumulate causing irritation and swelling and a dental hygiene appointment. The patients’ gums bleed and sometimes discharge a milky white material called exudate.
Our hygiene team at Deep Dental will get to work right away to remedy gingivitis by giving the subject’s teeth a thorough cleaning to remove excess plaque. Being diagnosed with gingivitis should help convince the patient to change their habits and step-up their brushing and flossing regime.
3. Early Periodontitis
When gingivitis is left untreated, it progresses to stage one periodontitis, also known as gum disease. Soft tissue around the teeth is inflamed and tender to the touch and may have turned a paler shade of pink as the blood supply is reduced.
The plaque around the patient’s teeth has hardened into a tougher, more damaging material called calculus or tartar, and this substance accelerates the damage. At this stage, the bone structures anchoring the patient’s teeth to his or her jaw are weakened, and they’re at much greater risk of tooth loss.
4. Moderate Periodontitis
Stage four periodontal disease is when the patient’s gums are seen to be visibly receding, exposing tender tooth enamel which can be more easily damaged and decayed. The hidden damage to the subject’s jawbone will start to become noticeable as his or her teeth loosen, become wobbly or even move position.
What’s more, at this point a discharge is likely to happen frequently and leave a strongly unpleasant taste in the patient’s mouth. This is a sign that infection has set in, and the risk to the patient’s teeth is now severe.
5. Advanced Periodontitis
In the advanced stage of periodontitis, the patient’s gums are visibly shrunken and large portions of his or her teeth are exposed. Many teeth are loose, even ones which look healthy, as the infection is now attacking the jawbone itself. Without treatment, tooth loss is inevitable.
In the early stages of periodontitis, intense cleaning and a course of antibiotics is usually enough to stop the disease from progressing and can help repair the damage done. However, the longer the condition remains untreated, the harder it is to remedy. Advanced periodontitis may require invasive dental surgery to clear away all traces of the disease, and even then, the damage may be irreversible.
The earlier the patients act, the quicker Deep Dental can restore their mouths to full health.



